Diabetic Retinopathy
Every year, many patients with diabetes are diagnosed with a potentially devastating eye disease known as diabetic retinopathy. At Delray Eye Associates, P.A., we are committed to helping people with diabetes maintain their eye health and sight.
What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
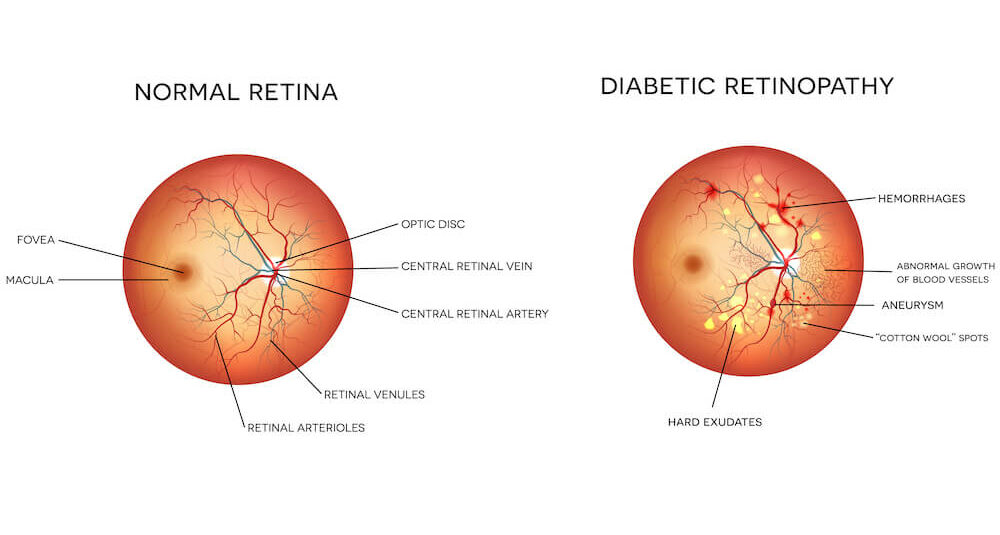
Diabetic retinopathy is a retinal disease that occurs in people with diabetes. Anyone who has diabetes can potentially develop diabetic retinopathy; however, not every diabetic is diagnosed with the disorder. Diabetic retinopathy is a result of increased blood sugar levels that damage the blood vessels in the retina, usually over the course of years. The longer a patient has diabetes, the more likely he or she is to develop this sight-threatening condition. There are two stages of the disease: nonproliferative retinopathy and proliferative retinopathy.
- Nonproliferative retinopathy is the early stage of the disease. High blood sugar levels cause the blood vessels in the retina to bleed or leak fluid. The retina may then swell and vision may become blurry.
- Proliferative retinopathy is the later stage of the disease. New blood vessels develop, or proliferate, on the retina’s surface. These vessels can break and bleed into the eye, form scar tissue that may detach the retina, or even cause a severe type of glaucoma. This form of the disease can lead to severe vision problems, including blindness.
Courtesy of the American Academy of Ophthalmology
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
Several symptoms can indicate the possible presence of diabetic retinopathy. Many people with diabetic retinopathy may have no symptoms at all, particularly in early cases, where vision preservation is most likely. Therefore, it is important that any patient with diabetes has a regular dilated eye exam. Those who struggle with reading or other close-up vision activities may be experiencing a symptom of the disease due to the collection of fluid in the macula, the central part of the retina. Double vision is another sign of potential diabetic eye disease. Any person with diabetes who is experiencing these symptoms should have a prompt eye examination.
To help diagnose and treat complications of diabetic retinopathy, an optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging test may help pinpoint any abnormal fluid indicating the need for treatment and/or close monitoring. Occasionally another exam known as fluorescein angiography may be performed. This test involves the injection of dye into a vein in the hand or arm. Once the dye travels through the bloodstream to the retina, the eye is photographed and the pictures are analyzed to determine whether the disease is present.
Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy
There are several treatment options for diabetic retinopathy.
- Laser Photocoagulation– In this procedure, laser energy may be applied directly to leaking areas of blood vessels, or used to inactivate outer areas of the retina to stop the growth of new blood vessels.
- Vitrectomy– If blood has leaked into the vitreous, a vitreoretinal surgeon may perform this operation in which the vitreous humor is removed and replaced with a saline liquid. This procedure is typically performed in cases in which the diabetic retinopathy has resulted in significantly impaired vision. Abnormal membranes may also be addressed and laser photocoagulation applied.
- Lucentis, Avastin, and Eylea– These drugs are frequently used to treat macular degeneration. They are sometimes prescribed to reduce the growth, bleeding and/or leakage of abnormal blood vessels in diabetic retinopathy patients.
Prevention of Diabetic Retinopathy
Everyone with diabetes should obtain an eye exam at least once a year because early diagnosis of the disease is crucial for preventing vision loss. People with diabetes must remain vigilant and immediately visit an eye care professional if they experience symptoms of blurred vision. In the meantime, there are steps they can take to minimize their risk of developing retinopathy. These include careful control of blood sugar and blood pressure levels, a healthy diet and exercise regimen, and adherence to their doctor’s instructions.
Contact Delray Eye Associates at (561) 498-8100 or (561) 734-0267 for more information or to schedule an appointment.
